Foreword / YouTube Video Review
These speakers were loaned to me to review by a viewer. I was not paid nor did I receive any other form of compensation for this review.
All my reviews are done on my own time with great care to give you all the best set of data and information I can provide in order to help you make a well-informed purchase decision. I offer this for free to all who are interested. In return, if you want to support this site please see the bottom of this review for ways you can help. It is greatly appreciated.
The review on this website is a brief overview and summary of the objective performance of this speaker. It is not intended to be a deep dive. Moreso, this is information for those who prefer “just the facts” and prefer to have the data without the filler. The video below has more discussion with respect to the technical merits and subjective notes I had during my listening sessions.
- DESIGN: 4-driver, 2 passive radiator, 3 way center channel, sealed enclosure
- CROSSOVER: 2nd order electro-acoustic at 2.5 kHz (tweeter), 2nd order @ 500 Hz (bass)
- HIGH FREQUENCY DRIVER: Coaxial 1" (25mm) AL-MAC™ Ceramic Dome with Oblate Spheroid Waveguide (OSW™) and Perforated Phase-Aligning (PPA™) Tweeter Lens, ferro-fluid damped / cooled, Patent Pending Dual Gap Motor Structure
- FREQUENCY RESPONSE ON-AXIS: ±2dB from 55 Hz - 23 kHz
- FREQUENCY RESPONSE 30° OFF-AXIS: ±2dB from 55 Hz - 17 kHz
- BASS FREQUENCY DRIVER : Two 7" (177mm) Ultra-HighExcursion CARBON-X™ Unibody Cone, Gen3 Active Ridge Technology (ART™) with Vertical Mounting System, Advanced SHOCK-MOUNT™ Isolation, and a 1.5” high-temp multi-layered voice coil with ventilated Apical™ former
- MIDRANGE FREQUENCY DRIVER: Coaxial 6” (152mm) AL-MAG™ Cone with SHOCK-MOUNT™ Isolation Mounting System, a 2” high-temp multi-layered voice coil with Apical™ former, Patented Dual-Sync™ Continuous Flux Motor
- SENSITIVITY ROOM / ANECHOIC: 94 dB / 91 dB
- LOW FREQUENCY EXTENSION: 37 Hz (DIN)
- SUITABLE AMPLIFIER POWER RANGE: 15 - 260 watts
- MAXIMUM INPUT POWER: 200 watts
- IMPEDANCE: Compatible with 8 ohms
- PASSIVE RADIATORS: Two 7" (177mm) Ultra-High-Excursion CARBON-X™ Unibody Cone, Gen3 Active Ridge Technology (ART™) with Vertical Mounting System, Advanced SHOCKMOUNT™ Isolation, Passive
- DIMENSIONS HXWXD: 8.9” x 35.7” x 12.9” (22.6cm x 90.8cm x 32.7cm)
- WEIGHT: 48 lbs (21.8 kg) each
- FINISHES: Piano Black, Black Walnut, Midnight Cherry, Walnut
As of this writing MSRP is approximately $2900.
CTA-2034 (SPINORAMA) and Accompanying Data
All data collected using Klippel’s Near-Field Scanner. The Near-Field-Scanner 3D (NFS) offers a fully automated acoustic measurement of direct sound radiated from the source under test. The radiated sound is determined in any desired distance and angle in the 3D space outside the scanning surface. Directivity, sound power, SPL response and many more key figures are obtained for any kind of loudspeaker and audio system in near field applications (e.g. studio monitors, mobile devices) as well as far field applications (e.g. professional audio systems). Utilizing a minimum of measurement points, a comprehensive data set is generated containing the loudspeaker’s high resolution, free field sound radiation in the near and far field. For a detailed explanation of how the NFS works and the science behind it, please watch the below discussion with designer Christian Bellmann:
IMPORTANT SETUP INFO: This speaker was measured with the reference point at the tweeter. Speaker was broken in. No grille on coaxial.
Measurements are provided in a format in accordance with the Standard Method of Measurement for In-Home Loudspeakers (ANSI/CTA-2034-A R-2020). For more information, please see this link.
CTA-2034 / SPINORAMA:
The On-axis Frequency Response (0°) is the universal starting point and in many situations it is a fair representation of the first sound to arrive at a listener’s ears.
The Listening Window is a spatial average of the nine amplitude responses in the ±10º vertical and ±30º horizontal angular range. This encompasses those listeners who sit within a typical home theater audience, as well as those who disregard the normal rules when listening alone.
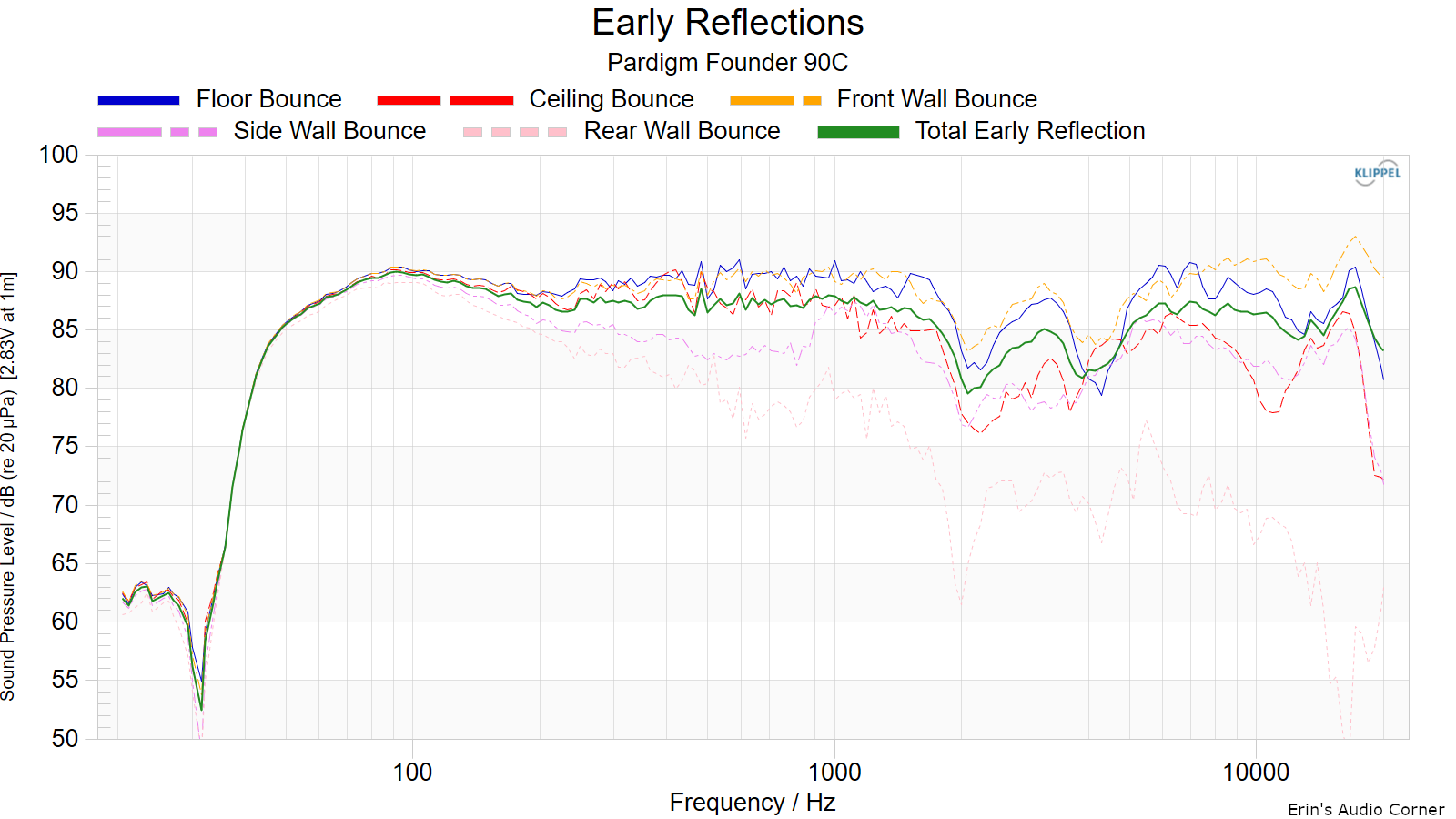
The Early Reflections curve is an estimate of all single-bounce, first-reflections, in a typical listening room.
Sound Power represents all of the sounds arriving at the listening position after any number of reflections from any direction. It is the weighted rms average of all 70 measurements, with individual measurements weighted according to the portion of the spherical surface that they represent.
Sound Power Directivity Index (SPDI): In this standard the SPDI is defined as the difference between the listening window curve and the sound power curve.
Early Reflections Directivity Index (EPDI): is defined as the difference between the listening window curve and the early reflections curve. In small rooms, early reflections figure prominently in what is measured and heard in the room so this curve may provide insights into potential sound quality.

Early Reflections Breakout:
Floor bounce: average of 20º, 30º, 40º down
Ceiling bounce: average of 40º, 50º, 60º up
Front wall bounce: average of 0º, ± 10º, ± 20º, ± 30º horizontal
Side wall bounces: average of ± 40º, ± 50º, ± 60º, ± 70º, ± 80º horizontal
Rear wall bounces: average of 180º, ± 90º horizontal
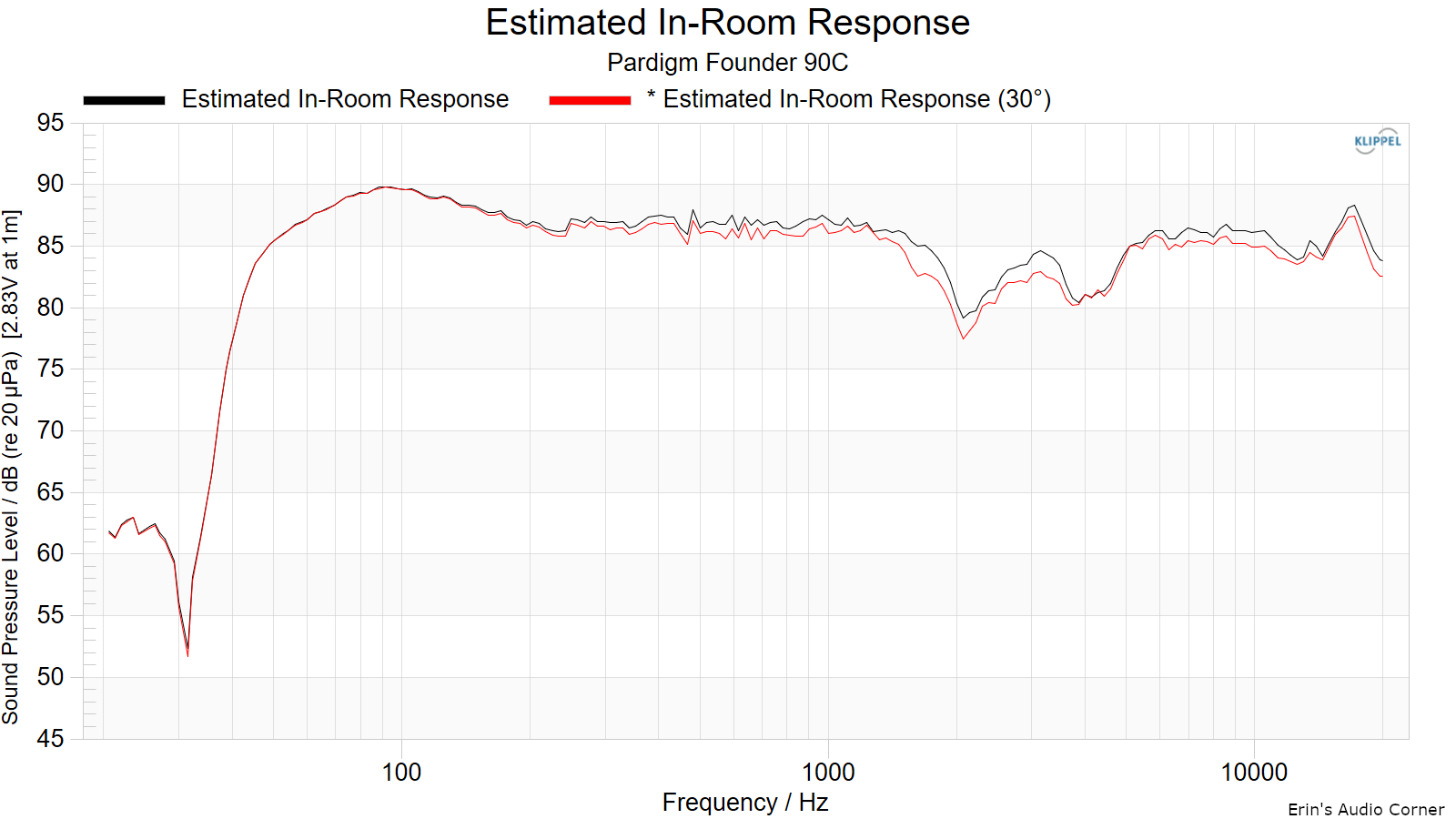
Estimated In-Room Response:
In theory, with complete 360-degree anechoic data on a loudspeaker and sufficient acoustical and geometrical data on the listening room and its layout it would be possible to estimate with good precision what would be measured by an omnidirectional microphone located in the listening area of that room. By making some simplifying assumptions about the listening space, the data set described above permits a usefully accurate preview of how a given loudspeaker might perform in a typical domestic listening room. Obviously, there are no guarantees, because individual rooms can be acoustically aberrant. Sometimes rooms are excessively reflective (“live”) as happens in certain hot, humid climates, with certain styles of interior décor and in under-furnished rooms. Sometimes rooms are excessively “dead” as in other styles of décor and in some custom home theaters where acoustical treatment has been used excessively. This form of post processing is offered only as an estimate of what might happen in a domestic living space with carpet on the floor and a “normal” amount of seating, drapes and cabinetry.
For these limited circumstances it has been found that a usefully accurate Predicted In-Room (PIR) amplitude response, also known as a “room curve” is obtained by a weighted average consisting of 12 % listening window, 44 % early reflections and 44 % sound power. At very high frequencies errors can creep in because of excessive absorption, microphone directivity, and room geometry. These discrepancies are not considered to be of great importance.
Horizontal Contour Plot (normalized):

Vertical Contour Plot (normalized):

Additional Measurements
Impedance

Response Linearity

Horizontal Frequency Response:

Vertical Frequency Response:

Step Response

Group Delay

Burst Decay
This data is full anechoic where most spectral decay type graphics are created using quasi-anechoic data. For more information on the differences between Burst Decay and Cumulative Spectral Decay (CSD) graphics please see Section 6.5 of the ARTA User Manual linked below. I would like to extend a professional "thank you" to Ivo Mateljan for this software.

Harmonic Distortion
Harmonic Distortion at 86dB @ 1m:

Harmonic Distortion at 96dB @ 1m:

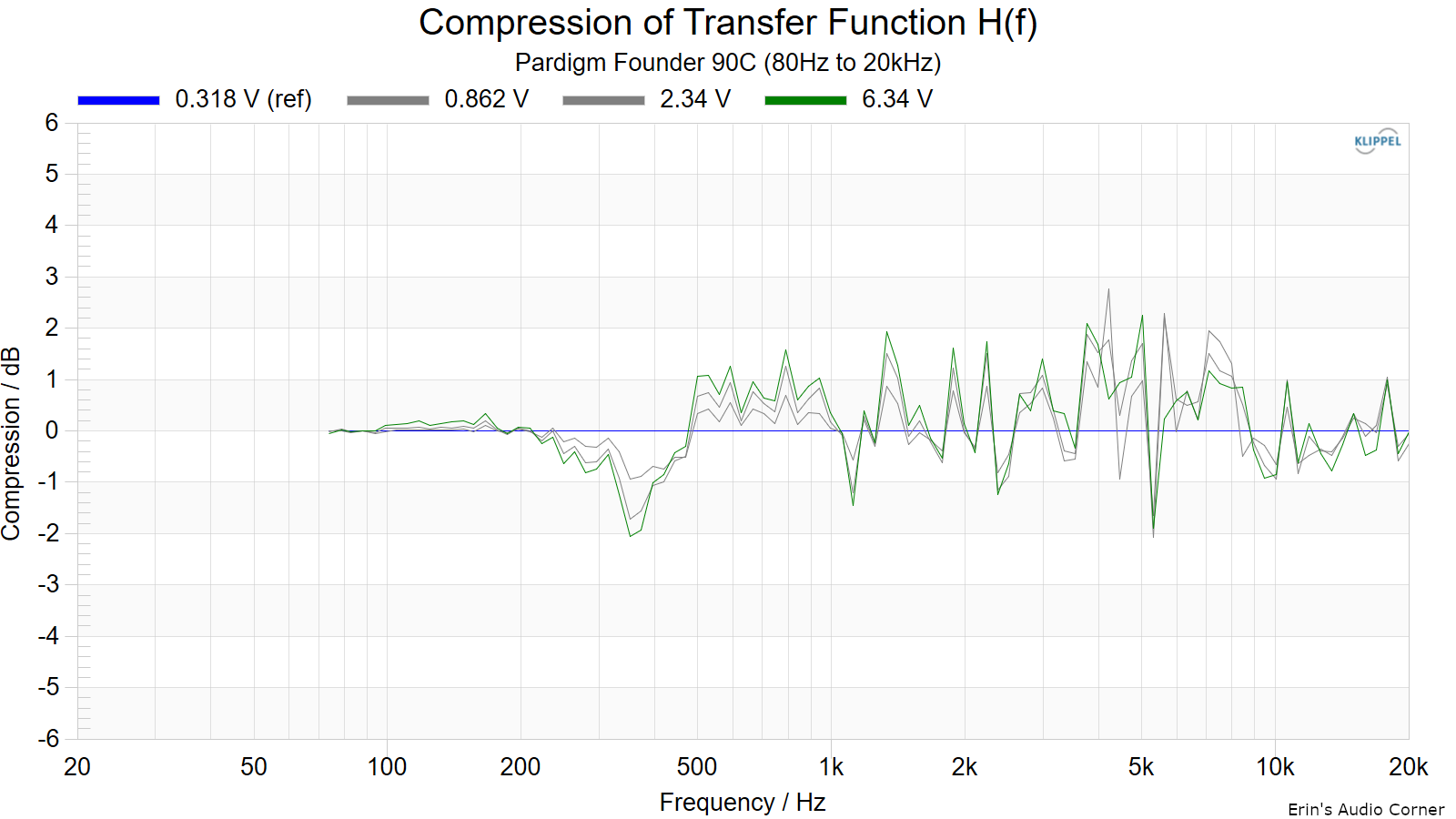
Dynamic Range (Instantaneous Compression Test)
The below graphic indicates just how much SPL is lost (compression) or gained (enhancement; usually due to distortion) when the speaker is played at higher output volumes instantly via a 2.7 second logarithmic sine sweep referenced to 76dB at 1 meter. The signals are played consecutively without any additional stimulus applied. Then normalized against the 76dB result.
The tests are conducted in this fashion:
- 76dB at 1 meter (baseline; black)
- 86dB at 1 meter (red)
- 96dB at 1 meter (blue)
- 102dB at 1 meter (purple)
The purpose of this test is to illustrate how much (if at all) the output changes as a speaker’s components temperature increases (i.e., voice coils, crossover components) instantaneously.

Multitone Distortion
The following tests are conducted at (4) approximate equivalent output volumes: 70/79/87/96dB @ 1 meter. The (4) voltages listed in the legend result in these SPL values. This test signal is dense, similar to pink noise and excites the entire spectrums listed below at the same time. The test signal lasts 30 seconds. This is different than the sine wave test signal used to measure frequency response. The purpose of this distortion and compression test is to illustrate how much (if at all) the output changes as a speaker’s components temperature increases (i.e., voice coils, crossover components) over time.
Given the test signal is similar to pink noise and exciting the entire spectrum at the same time I also include compression results, which is captured at the same time distortion is captured. Sometimes these results differ from the compression results you see above (namely with powered designs incorporating DSP-based limiting).
Note: The KLIPPEL software shows compression in the positive scale.
The test was conducted in (3) manners:
- Full bandwidth (20Hz to 20kHz)
- 80Hz to 20kHz
The reason for the two measurements is to simulate running the speaker full range vs using a high-pass filter at 80Hz. However, note: the 2nd test low frequency limit at 80Hz is a “brick wall” and doesn’t quite emulate a standard filter of 12 or 24dB/octave. But… it’s close enough to illustrate the point.
- Full bandwidth (20Hz to 20kHz)


- 80Hz to 20kHz

Parting / Random Thoughts
See video linked above for full subjective and objective analysis. An AI-generated summarized transcript is provided below:
- The Paradigm 90C is a 3-way center channel speaker priced around $2,899
- Uses a coaxial midrange and tweeter, flanked by two 7" midbass drivers and two passive radiators
- Loaned by a viewer for review — big thanks to them
- Background on center channel issues
- Previous video explained how 2-way MTM designs suffer from off-axis comb filtering
- Causes intelligibility problems in multi-seat home theaters
- Modern mixes already have low vocal clarity — flawed center channels make it worse
- Expectations vs reality with the Paradigm 90C
- Expectations were high due to the 3-way coaxial design
- However, subjective listening revealed poor clarity and weak upper midrange
- Sound was lifeless and lacked attack, even on-axis
- Off-axis performance also disappointing — still dull and unclear
- Subjective impressions
- Good low-end extension — reaches about 50 Hz in-room
- Bass was strong and satisfying
- Major issue: lack of definition and clarity in upper mids and treble
- Dialogue sounded muffled; closed captioning still needed
- Measurement data from Klippel NFS
- On-axis frequency response:
- F3 at 54.4 Hz, F10 at 41 Hz
- Average sensitivity ~90 dB
- Response reasonably neutral below 2 kHz, but major degradation from 2–5 kHz
- Shows poor coaxial driver behavior — likely flawed design (note that Audioholics show similar issues in their review of the 70LCR)
- On-axis frequency response:
- CTA-2034 spinorama and directivity
- Directivity is inconsistent, especially in mid-to-treble transition
- Reflections and direct sound differ — cannot fix with EQ
- Causes midrange suckout and tonal shift in side seats
- Estimated in-room response
- Good bass bump and extension
- Significant upper midrange dip leads to dull, veiled sound
- Poor slope control in higher frequencies
- Horizontal radiation
- 20° off-axis listeners experience tonal shifts and reduced clarity
- Reflections exacerbate the issue for side seating
- Vertical radiation
- Reasonably good — about ±40° window
- Distortion and compression
- High distortion levels, especially for a speaker of this size
- Midrange distortion well above expectations
- Suggests design flaws or poor crossover implementation
- Multi-tone tests and compression confirm similar issues
- Dynamic range compression especially bad in midrange
- Impedance and amplification
- Nominal impedance ~4 ohms
- EPDR dips to ~1.6 ohms — needs high-current amplifier
- Class AB users should ensure amp can handle 2 ohm loads
- Using high crossover (80–100 Hz) could mitigate strain
- Final thoughts
- Speaker has good bass, high sensitivity, decent vertical dispersion
- But major shortcomings in clarity and midrange performance
- Not acceptable for its $2,900 price point
- Objective and subjective data align — this speaker needs improvement
- Open to doing more reviews like this if viewers find value
Support / Contribute
If you find this review helpful and want to help support the cause that would be AWESOME! There are a few ways you can do so below. Your support helps me pay for new items to test, hardware, miscellaneous items needed for testing, new speakers to review and costs of the site’s server space and bandwidth. Any help is very much appreciated.
Join my Patreon: Become a Patron!
Shopping
If you are shopping at any of the following stores then please consider using my generic affiliate links below to make the purchase through.
Purchases through these links can earn me a small commission - at no additional cost to you - and help me continue to provide the community with free content and reviews. Doesn’t matter if it’s a TV from Crutchfield, budget speakers from Audio Advice or a pair of socks from Amazon, just use the link above before you make your purchase. Thank you!
